使用 npm-check-updates 快速升级前端项目 package.json 依赖版本
- 前端开发
- 2020-10-29
- 2583热度
- 0评论
通过使用 npm outdated 和 npm update 命令,可以对前端项目中的第三方依赖版本进行分析与升级。但他们可用的参数较少,有些过于简单。
在 Microsoft Visual Code 编辑器中,当鼠标停留在依赖行并保持不动时,它会去查询该行依赖的最新版本。这在对单个的第三方依赖版本升级上会有比较简单快捷的辅助。
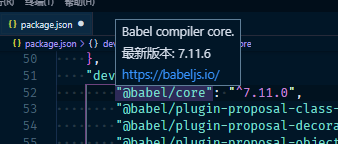
对于依赖众多的中大型项目,其第三方依赖包可能多达上百个。当希望进行大的版本和依赖升级时,手动逐个去检测和修改版本号也会是一个比较麻烦的事情。利用 npm-check-updates 可以协助应对这种场景。它是一个帮助你升级 package.json 中的依赖至最新版本,并且提供多个参数以满足不同的升级需求。
1 使用 npm-check-updates
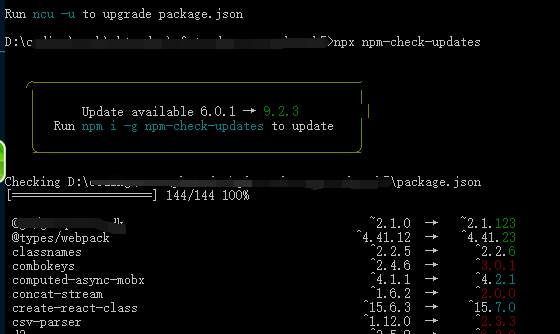
npm-check-updates 的使用很简单。进入项目目录中,然后使用 npx 执行其命令,即可进行最新依赖版本的检测:
npx npm-check-updates
当然,你也可以全局安装它,然后就可以使用其提供的 ncu 命令:
npm i -g npm-check-updates
ncu --help
默认情况下,执行 ncu -u 即可将 package.json 中的所有第三方依赖版本修改为其最新的版本。
一些示例:
# 交互式升级:每一个依赖的修改都需手工确认
ncu -u -i
# 只更新补丁版本 -- 按指定的<target>级别更新。target 可选值:latest, newest, greatest, minor, patch
ncu -u --target patch
# 仅更新 devDependenties 下的依赖。dep 可选参数: prod, dev, peer, optional, bundle(多个可用逗号分隔)
ncu -u --dep dev
# 仅更新包名称包含 react 字符串的依赖
ncu -u --filter /react/
# 不更新包名称包含 electron 字符串的依赖
ncu -u --reject /electron/
# 检查更新是否可以通过测试(npm test),并指定项目管理器为 yarn
ncu -u --doctor -p yarn
2 调用 npm-check-updates 模块化 API 接口方式
此外,你也可以通过命令行方式调用其 API 接口,以实现定制的辅助工具或脚本:
const ncu = require('npm-check-updates');
const upgraded = await ncu.run({
// Pass any cli option.
// Defaults:
jsonUpgraded: true,
silent: true
});
console.log(upgraded)
3 npm-check-updates 相关参数参考
Usage: cli [options] [filter]
[filter] is a list or regex of package names to check (all others will be ignored).
Options:
--concurrencyMax number of concurrent HTTP requests to registry. (default: 8)
--configFilePathDirectory of .ncurc config file (default: directory of packageFile).
--configFileNameConfig file name (default: .ncurc.{json,yml,js})
--cwdWorking directory in which npm will be executed.
--depCheck one or more sections of dependencies only: prod, dev, peer, optional, bundle (comma-delimited).
--deprecated Include deprecated packages.
--doctor Iteratively installs upgrades and runs tests to identify breaking upgrades. Run "ncu --doctor" for detailed help. Add "-u" to execute.
--enginesNode Include only packages that satisfy engines.node as specified in the package file.
-e, --errorLevelSet the error level. 1: exits with error code 0 if no errors occur. 2: exits with error code 0 if no packages need updating (useful for continuous integration). (default: 1)
-f, --filterInclude only package names matching the given string, comma-or-space-delimited list, or /regex/.
-g, --global Check global packages instead of in the current project.
--greatest DEPRECATED. Renamed to "--target greatest".
-i, --interactive Enable interactive prompts for each dependency; implies -u unless one of the json options are set,
-j, --jsonAll Output new package file instead of human-readable message.
--jsonDeps LikejsonAllbut only listsdependencies,devDependencies,optionalDependencies, etc of the new package data.
--jsonUpgraded Output upgraded dependencies in json.
-l, --loglevelAmount to log: silent, error, minimal, warn, info, verbose, silly. (default: "warn")
-m, --minimal Do not upgrade newer versions that are already satisfied by the version range according to semver.
-n, --newest DEPRECATED. Renamed to "--target newest".
-p, --packageManagernpm, yarn (default: "npm")
-o, --ownerChanged Check if the package owner changed between current and upgraded version.
--packageDataPackage file data (you can also use stdin).
--packageFilePackage file location (default: ./package.json).
--preInclude -alpha, -beta, -rc. (default: 0; default with --newest and --greatest: 1).
--prefixCurrent working directory of npm.
-r, --registryThird-party npm registry.
--removeRange Remove version ranges from the final package version.
--semverLevelDEPRECATED. Renamed to --target.
-s, --silent Don't output anything (--loglevel silent).
-t, --targetTarget version to upgrade to: latest, newest, greatest, minor, patch.
--timeoutGlobal timeout in milliseconds. (default: no global timeout and 30 seconds per npm-registery-fetch).
-u, --upgrade Overwrite package file with upgraded versions instead of just outputting to console.
-x, --rejectExclude packages matching the given string, comma-or-space-delimited list, or /regex/.
-V, --version output the version number
-h, --help display help for command