如何快速了解项目源文件的构成?基于 Node.js 实现项目源代码数据统计工具
- 前端开发
- 2022-11-15
- 1258热度
- 0评论
摘要
当希望了解一个项目的代码规模时,首先可能会想对项目的源文件数量、代码行数等做一下数据统计。本文介绍了CLOC代码统计工具,以及基于 Node.js 实现个性化项目代码统计分析的实现思路。
当希望了解一个项目的代码规模时,首先可能会想对项目源文件的数量、类型分布、代码行数等做一下数据统计。使用 Linux/git 命令可以满足简单的统计需求,使用流行的 cloc 工具可以实现详细的源代码分析数据。此外也可以使用 Node.js 编码简单的实现个性化数据收集与分析。
1 使用 Linux 命令实现源文件代码行数统计
简单的代码行数统计可以通过 linux 自带的命令实现。示例:
# 统计 src 目录下 ts、tsx、scss 源文件的行数
find ./src "(" -name "*.ts" -or -name "*.tsx" -or -name "*.scss" ")" -print | xargs wc -l
如果项目使用 git 管理,还可以使用 git 命令统计提交者的代码行数等。示例(Linux/MacBook):
# 统计某个人的代码提交行数
git log --author="renxia" --pretty=tformat: --numstat | awk '{ add += $1; subs += $2; loc += $1 - $2 } END { printf "added lines: %s, removed lines: %s, total lines: %s\n", add, subs, loc }' -
# 统计每个人的代码提交行数
git log --format='%aN' | sort -u | while read name; do echo -en "$name\t"; git log --author="$name" --pretty=tformat: --numstat | awk '{ add += $1; subs += $2; loc += $1 - $2 } END { printf "added lines: %s, removed lines: %s, total lines: %s\n", add, subs, loc }' -; done
2 使用 cloc 代码行数统计工具
当希望得到更为全面的统计数据时,可能会通过搜索引擎检索了解到代码行数统计工具cloc(Count lines of code)。
cloc 基于 Perl 语言开发,支持多种系统环境下的快捷安装。安装 cloc 的方法参考:
npm install -g cloc # https://www.npmjs.com/package/cloc
sudo apt-get install cloc # Debian, Ubuntu
sudo yum install cloc # Red Hat, Fedora
sudo pacman -S cloc # Arch
sudo pkg install cloc # FreeBSD
sudo port install cloc # Mac OS X with MacPorts
cloc 经过多年的开源社区迭代,功能已相当丰富,支持数十种常见编程语言的源代码和注释分析与行数统计,支持按目录、文件、甚至压缩文件、git commit hash 等各种方式进行代码行数统计、diff 差异对比分析等。其支持的命令行参数多达数十个。
cloc 的一些用法示例:
# 查看支持的编程语言类型
cloc --show-lang
# 统计 src 和 plugins 目录
cloc src plugins
# 统计 src 目录,按 `代码+注释+空行` 为分母计算输出为百分比格式
cloc --by-percent cmb src
# 统计当前目录下 master.zip 压缩文件
cloc master.zip
# 统计 src/lzwme.ts 文件
cloc src/lzwme.ts
# 统计两次提交(git commitId head)之间的文件与源代码差异
cloc --diff 22e7cf83 ef25fe47
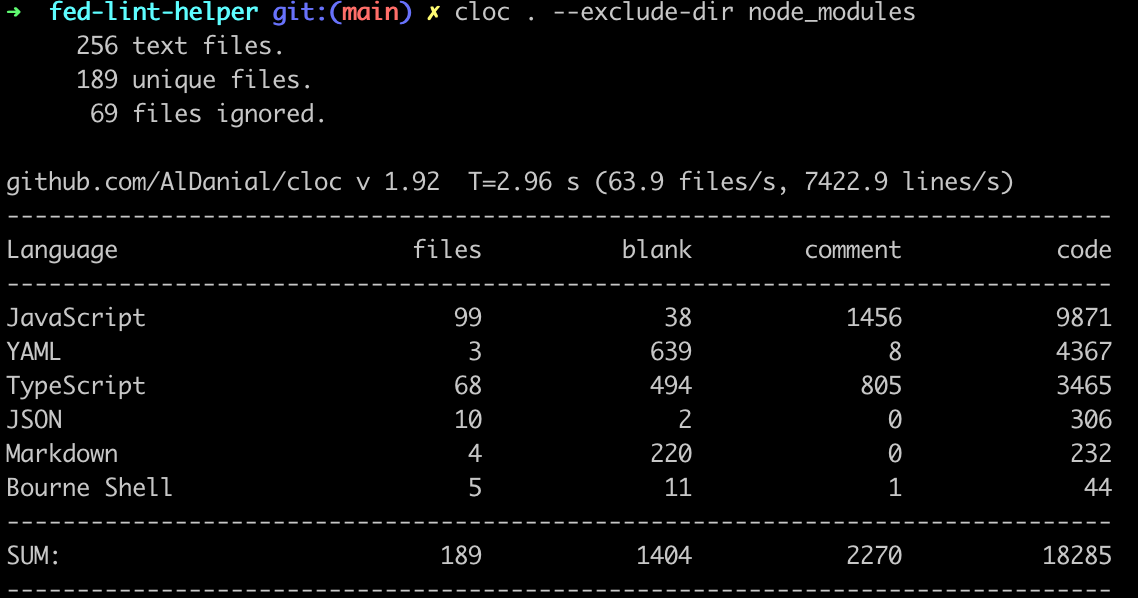
cloc 工具以代码行数统计为核心目标,提供了多样化的参数,可以实现绝大部分针对代码行数相关的数据统计需求。
但是对于如文件大小统计、按大小或行数输出 Top N、输出重复文件列表等个性化的需求,则仍需编码实现。
3 基于 Node.js 实现个性化的项目源代码统计
在不考虑归档文件、各种编程语言的注释解析、git diff 等复杂场景的前提下,项目代码统计可以简化为文本类文件的数量汇总、大小与行数计算,于是自行编码也可以简单的实现个性化的项目源代码数据统计。其逻辑实现大致包含如下几个要点:
- 源文件扫描,得到文件列表
- 文件分类、大小与行数计算
- 重复文件统计
- 数据汇总与打印
- more...
近期在一个前端开发辅助工具项目中,基于以上几个要点,使用 Node.js 尝试实现了简单的项目源代码数据统计功能。下面尝试对相关主要逻辑实现进行逐一分析。
3.1 项目源文件快速扫描
使用 Node.js 的 fs 模块可以对指定的目录进行文件扫描。但当涉及规则过滤等参数处理时,其实现起来较为繁琐。
这里使用了 fast-glob 库实现指定目录的源文件扫描。示例:
// 使用 fast-glob 扫描 src 和 plugins 目录下的 ts 和 tsx 文件
import glob from 'fast-glob';
const rootDir = process.cwd();
const src = ['src', 'plugins'];
const pattern = '**/*.{ts,tsx}';
const exclude = ['**/node_modules/**'];
const fileList = await glob(
src.map(src => `${src}/${pattern}`),
{ cwd: rootDir, absolute: true, ignore: exclude }
);
上面示例展示的逻辑为使用 fast-glob 扫描 src 和 plugins 目录下的 ts 和 tsx 文件。将指定目录、匹配规则、过滤规则等变量参数化,即可实现可定制的目录文件扫描方法。
3.2 文件分类、大小与行数计算
遍历目录扫描得到的文件列表,按文件后缀分类,计算文件大小、行数、md5等信息并缓存,即可得到所有源文件的基本信息。示例:
const result = {
startTime: Date.now(),
endTime: 0,
total: 0,
totalSize: 0,
totalLine: 0,
totalBlank: 0,
topNByLine: [] as string[],
topNBySize: [] as string[],
exts: {} as Record<
string,
{
total: number;
totalSize: number;
totalLine: number;
totalBlank: number;
list: { filepath: string; line: number; blank: number; stat: Stats }[];
}
>,
};
//const fileList = getFileList(...);
// 所有文件按路径的映射缓存
const allFilesInfo = {} as { [filepath: string]: { filepath: string; line: number; md5: string; stat: Stats } };
result.total = fileList.length;
for (const filepath of fileList) {
let ext = extname(filepath).replace(/^./, '').toLowerCase();
// 单元测试文件独立统计
if (filepath.endsWith(`.test.${ext}`)) ext = `test.${ext}`;
else if (filepath.endsWith(`.spec.${ext}`)) ext = `spec.${ext}`;
const fileStat = await promises.stat(filepath);
const item = { filepath, line: 0, blank: 0, md5: md5(filepath), stat: fileStat };
allFilesInfo[filepath] = item;
result.totalSize += fileStat.size;
// 文件类型分类统计
if (!result.exts[ext]) result.exts[ext] = { total: 0, totalSize: 0, totalLine: 0, totalBlank: 0, list: [] };
result.exts[ext].list.push(item);
result.exts[ext].total++;
result.exts[ext].totalSize += fileStat.size;
// 文本文件,统计行数
if (isTextFile(filepath)) {
const content = await promises.readFile(filepath, 'utf8');
// 不计算首尾的空格与空行
const contentLines = content.trim().split('\n');
item.line = contentLines.length;
item.blank = contentLines.filter(line => line.trim() === '').length;
result.exts[ext].totalLine += item.line;
result.exts[ext].totalBlank += item.blank;
result.totalLine += item.line;
result.totalBlank += item.blank;
}
}
上面示例代码包含了如下几个要点:
- 文件总数统计
- 计算并统计文件大小、md5(用于重复文件比对)
- 按文件后缀进行分类
- 仅对文本文件统计行数
- 忽略文件首尾的空格与空行
3.3 统计数据结果打印
通过 console 输出打印信息,需注意数据格式的处理。示例:
const { green, cyanBright, magentaBright } = color;
const extsList = Object.entries(result.exts).sort((a, b) => b[1].total - a[1].total);
const widths = { row: 70, ext: 10, sep: 15 };
const statsInfo = [];
for (const [ext, list] of extsList) {
statsInfo.push(
[
cyanBright(padSpace(ext, widths.ext)),
magentaBright(padSpace(formatQty(list.total), widths.sep)),
green(padSpace(formatQty(list.totalBlank), widths.sep)),
green(padSpace(formatQty(list.totalLine), widths.sep)),
green(padSpace(formatMem(list.totalSize), widths.sep)),
].join('')
);
}
console.log(statsInfo);
其要点主要有:
- 文件类型按数量排序
- 使用
''.padStart和''.padEnd实现列数据对齐(padSpace) - 代码行数数据千分位处理(
formatQty) - 文件大小数据格式化处理(
formatMem)
此外,也可以将结果数据输出至文件以便进一步分析使用。
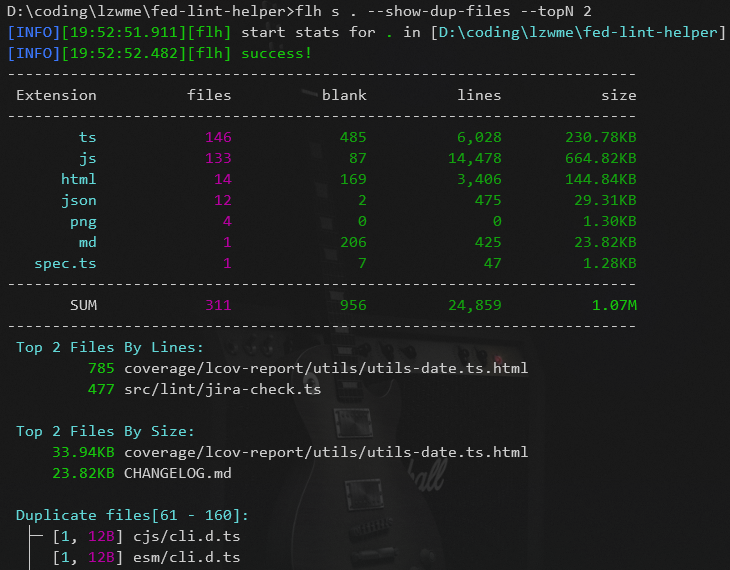
3.4 个性化数据统计:TopN、重复文件等
基于文件遍历时得到的文件大小、行数信息,可进行降序排序得到 TopN 列表,基于文件 md5 信息,可统计重复文件数据。
按文件大小、行数 TopN 统计示例:
const topN = 50; // 可由输入参数指定
if (topN > 0) {
result.topNByLine = fileList.sort((a, b) => allFilesInfo[b].line - allFilesInfo[a].line).slice(0, topN);
result.topNBySize = fileList.sort((a, b) => allFilesInfo[b].stat.size - allFilesInfo[a].stat.size).slice(0, topN);
const topNfilesByLine = result.topNByLine.map(
d => `${greenBright(padSpace(formatQty(allFilesInfo[d].line), 10))} ${showFullPath ? d : fixToshortPath(d, rootDir)}`
);
statsInfo.push(` ${cyanBright(`Top ${topN} Files By Lines:`)}${fileListToString(topNfilesByLine, '')}`);
const topNfilesBySize = result.topNBySize.map(
d => `${greenBright(padSpace(formatMem(allFilesInfo[d].stat.size), 10))} ${showFullPath ? d : fixToshortPath(d, rootDir)}`
);
statsInfo.push(` ${cyanBright(`Top ${topN} Files By Size:`)}${fileListToString(topNfilesBySize, '')}`);
}
重复文件统计示例:
// 重复文件统计
const filepathByMd5 = {} as { [md5: string]: string[] };
const duplicates = new Set< string>();
Object.values(allFilesInfo).forEach(d => {
if (!filepathByMd5[d.md5]) {
filepathByMd5[d.md5] = [d.filepath];
} else {
filepathByMd5[d.md5].push(d.filepath);
duplicates.add(d.md5);
}
});
if (duplicates.size > 0) {
// 按重复文件数量降序
const list = [...duplicates].map(d => filepathByMd5[d]).sort((a, b) => b.length - a.length);
result.duplicates = list;
const duplicatesTotal = list.reduce((total, item) => total + item.length, 0);
statsInfo.push(cyanBright(` Duplicate files[${list.length} - ${duplicatesTotal}]:`));
list.forEach(item => {
item = item.map(d => `${showFullPath ? d : fixToshortPath(d, options.rootDir)} [${magentaBright(allFilesInfo[d].line)}]`);
statsInfo.push(` ├─ ${item.join('\n │ ')}\n`);
});
}
3.5 小结
上面通过代码示例展示了项目源代码行数统计的一些实现细节,在逻辑上是比较简单的。
其具体的完整实现可参考:https://github.com/lzwme/fed-lint-helper/blob/main/src/stats/index.ts
如有兴趣,也可通过如下命令进行体验:
npx @lzwme/fed-lint-helper stats src