前端实现 gzip 文件与文本压缩的方法
- 前端开发
- 2021-08-29
- 2123热度
- 0评论
目录
[隐藏]
1 Node.js 中的 zilb 库与文件压缩
zlib 支持的三种压缩算法:gzip、deflate、brotli。基础用法示例:
import zlib from 'zlib';
function zip(str, encoding = 'gzip') {
str = typeof str === 'string' ? str : JSON.stringify(str);
if (encoding === 'deflate') return zlib.deflateSync(str);
if (encoding === 'brotli') return zlib.brotliCompressSync(str);
return zlib.gzipSync(str);
}
function upzip(buffer, encoding = 'gzip') {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
buffer instanceof Buffer ? buffer : Buffer.from(buffer);
if (encoding === 'gzip') {
// const buf = zlib.gunzipSync(buffer);
zlib.gunzip(buffer, (error, buf) => {
resolve({ error, buffer: error ? null : buf });
});
} else if (encoding === 'deflate') {
// const buf = zlib.inflateSync(buffer);
zlib.inflate(buffer, (error, buf) => {
resolve({ error, buffer: error ? null : buf });
});
} else if (encoding === 'brotli') {
// const buf = zlib.brotliDecompressSync(buffer);
zlib.brotliDecompress(buffer, (error, buf) => {
resolve({ error, buffer: error ? null : buf });
});
}
});
}
上面是 gzip、deflate、brotli 三种不同压缩算法的简单实现。其压缩效率如何呢?我们写个脚本来简单测试一下:
function genRandomStrs(length = 100, range = 32) {
const list = [];
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
list.push(String.fromCharCode(Math.ceil(Math.random() * range) + 32));
}
return list.join('');
}
async function zlibTest() {
const charsRange = [5, 15, 30, 90];
const testDataLens = [100, 1_000, 10_000, 100_000]; // 1_000_000
const algorithmList = ['gzip', 'deflate', 'brotli'];
const stats = {};
for (const range of charsRange) {
const item = stats[`charsRange-` + range] = {};
for (const len of testDataLens) {
const testStr = genRandomStrs(len, range);
if (!item.size) item.size = [];
item.size.push(len);
for (const algo of algorithmList) {
const buf = zip(testStr, algo);
const cLen = buf.toString().length;
const rate = Math.ceil(100 * cLen / len) + '%';
if (!item[algo]) item[algo] = [];
item[algo].push(rate);
// const d = await upzip(buf, algo);
}
}
}
console.log(stats);
}
zlibTest();
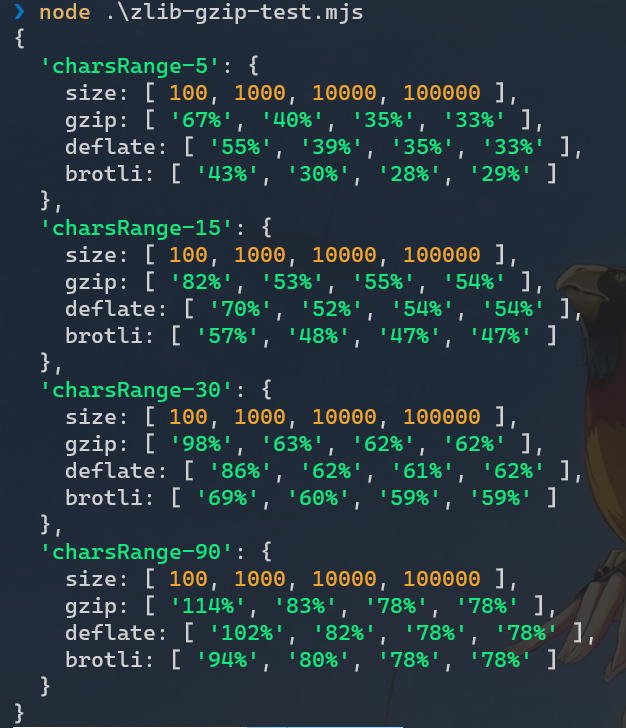
可以看到:
- 字符范围较小(重复度高)时,压缩效率依次为:
brotli>deflate>gzip - 相同条件下,文本越大(重复字符越多),压缩率越高
- 在文本范围较大时,压缩效率基本一致。
简单来说就是重复字符串越多,可压缩率越高。如果条件允许,选择 brotli 是较为合适的,但 gzip 在各场景下具有更好的通用性支持。
2 浏览器中使用第三方库 pako 实现 zip 压缩
一个支持浏览器中使用的 zlib 实现库,声称比 Node.JS 12、14 自带的 zlib 库都要快。
以下为一个在浏览器端实现文本 zip、unzip 压缩的示例。
import pako from 'pako';
// 也可以通过在页面中直接加载 CDN 的脚本测试
// <script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/pako/1.0.10/pako.min.js"></script>
function gzip(str) {
if (!str) return '';
if (typeof str !== str) str = JSON.stringfiy(str);
// 返回值为 utf16 编码,浏览器中对该编码字符串的读写可能会出现异常
// 这里也可以用 pako.zip,它是对 pako.deflate 的一个包装方法
const compressed = pako.deflate(str, {to: 'string'});
// 转换为 base64 编码
constt strBase64 = btoa(compressed);
return strBase64;
}
function unGzip(strBase64) {
// 也可以用 pako.ungzip,它们执行的是相同的方法逻辑
return pako.inflate(atob(strBase64), {to: 'string'});
}
更多细节可查阅其官方文档:http://nodeca.github.io/pako/
3 使用 compressing 实现文件夹的压缩与解压缩
上面分析了基于 zlib 的文件压缩方案。对于文件夹的压缩,则涉及对目录及子目录的文件遍历和全部文件归档,需要处理的细节较多。我们可以借助第三方工具包来简单的实现相关需求。
compressing 是一个相对比较流行的 Node.js 压缩与解压缩工具包,其提供的 API 简单易用。以下为相关示例:
import compressing from 'compressing';
// zip 压缩一个目录
compressing.zip.compressDir('./lzwme-test', 'lzwme-test.zip').then(() => console.log('success')).catch(e => console.error(e.stack));
// zip 解压
compressing.zip.uncompress('lzwme-test.zip', './lzwme-test').then(() => console.log('success')).catch(e => console.error(e.stack));
// tar 目录归档
compressing.tar.compressDir('./lzwme-test', 'lzwme-test.tar').then(() => console.log('success')).catch(e => console.error(e.stack));
// tar 归档解压
compressing.tar.uncompress('lzwme-test.tar', './lzwme-test').then(() => console.log('success')).catch(e => console.error(e.stack));
// gzip 压缩
compressing.gzip.compressFile('./lzwme-test.tar', 'lzwme-test.tar.gz').then(() => console.log('success')).catch(e => console.error(e.stack));
// gzip 解压
compressing.gzip.uncompress('lzwme-test.tar.gz', './lzwme-test').then(() => console.log('success')).catch(e => console.error(e.stack));
// tgz 压缩与解压(先 tar 对文件夹归档,再 gzip 对 tar 文件压缩)
compressing.tgz.compressDir('./lzwme-test', 'lzwme-test.tar.gz').then(() => console.log('success')).catch(e => console.error(e.stack));
// tgz 解压
compressing.tgz.uncompress('lzwme-test.tar.gz', './lzwme-test').then(() => console.log('success')).catch(e => console.error(e.stack));
4. 使用 JSZip 实现浏览器中的 zip 文件压缩
JSZip 支持在纯浏览器端实现文件的 zip 压缩与下载。其 API 也简单易懂。其也支持 Node.js 下使用。
示例:
import JSZip from 'jszip';
const zip = new JSZip();
zip.file("Hello.txt", "Hello World\n");
const img = zip.folder("images");
img.file("smile.gif", imgData, {base64: true});
zip.generateAsync({type:"blob"})
.then(function(content) {
// see FileSaver.js
saveAs(content, "example.zip");
});
更为详细的用法可参考其官方示例:https://stuk.github.io/jszip/documentation/examples.html